Clock signals
Table of contents
Clock signal
Clock signal is a periodic signal and its ON time and OFF time need not be the same. You can represent the clock signal as a square wave, when both its ON time and OFF time are same. This clock signal is shown in the following figure.
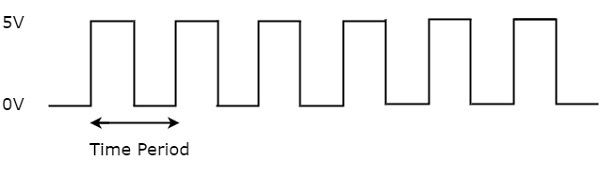
In the above figure, square wave is considered as clock signal. This signal stays at logic High (5V) for some time and stays at logic Low (0V) for equal amount of time. This pattern repeats with some time period. In this case, the time period will be equal to either twice of ON time or twice of OFF time.
You can represent the clock signal as train of pulses, when ON time and OFF time are not same. This clock signal is shown in the following figure.
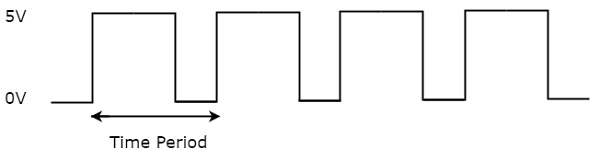
In the above figure, train of pulses is considered as clock signal. This signal stays at logic High (5V) for some time and stays at logic Low (0V) for some other time. This pattern repeats with some time period. In this case, the time period will be equal to sum of ON time and OFF time.
The reciprocal of the time period of clock signal is known as the frequency of the clock signal. All sequential circuits are operated with clock signal. So, the frequency at which the sequential circuits can be operated accordingly the clock signal frequency has to be chosen.
Types of triggering
Following are the two possible types of triggering that are used in sequential circuits.
- Level triggering
- Edge triggering
Level triggering
There are two levels, namely logic High and logic Low in clock signal. Following are the two types of level triggering.
- Positive level triggering
- Negative level triggering
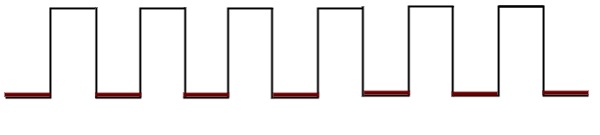
If the sequential circuit is operated with the clock signal when it is in Logic High, then that type of triggering is known as Positive level triggering. It is highlighted in below figure.
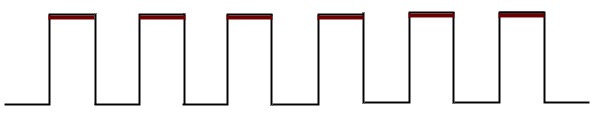
If the sequential circuit is operated with the clock signal when it is in Logic Low, then that type of triggering is known as Negative level triggering. It is highlighted in the following figure.
Edge triggering
There are two types of transitions that occur in clock signal. That means, the clock signal transitions either from Logic Low to Logic High or Logic High to Logic Low.
Following are the two types of edge triggering based on the transitions of clock signal.
- Positive edge triggering
- Negative edge triggering
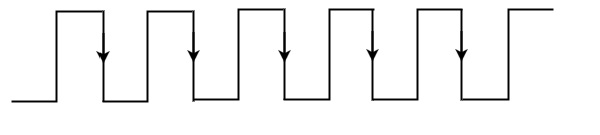
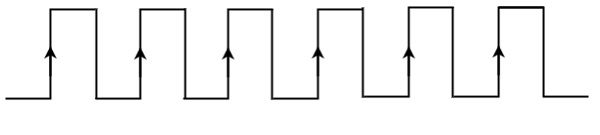
If the sequential circuit is operated with the clock signal that is transitioning from Logic Low to Logic High, then that type of triggering is known as Positive edge triggering. It is also called as rising edge triggering. It is shown in the following figure.
If the sequential circuit is operated with the clock signal that is transitioning from Logic High to Logic Low, then that type of triggering is known as Negative edge triggering. It is also called as falling edge triggering. It is shown in the following figure.