Race conditions
Table of contents
Introduction
Before getting into the race around condition, let us have a look at the JK flip-flop’s truth table.
| Clock Input | Inputs | Outputs | Comments | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | K | Q | Q’ | ||
| 0 | X | X | Same as previous | Same as previous | No change |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Same as previous | Same as previous | No change |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | Reset |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Set |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Opposite of previous | Opposite of previous | Toggle |
Here, Q is the present state and Q’ is the next state. As you can see, when J, K and Clock are equal to 1, toggling takes place, i.e. The next state will be equal to the complement of the present state.
Now, let us look at the timing diagram of JK flip-flop.
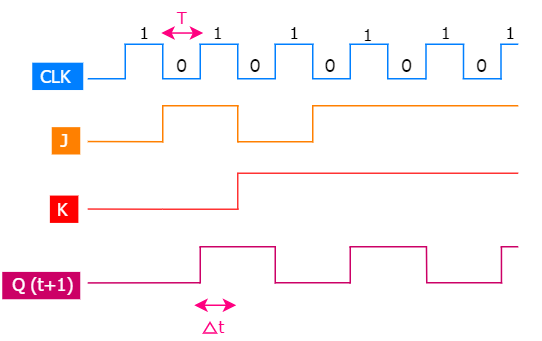
Here, T is the time period of the clock whereas delta t is the propagation delay. The delay between input and output is called a propagation delay.
This is what was expected, but the output may not be like this all the time. This is where Race around condition comes into the play.
Let us look at the timing diagram of JK flip-flop when the race around condition is considered.
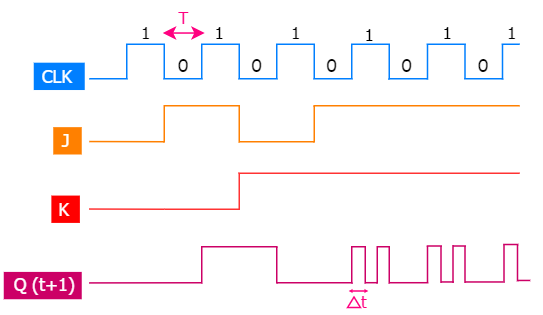
As you already know, when J, K and Clock are equal to 1, toggling takes place. Here, propagation delay has also been reduced, so the output will be given out at the instant input is given. So there is a toggling again. Therefore, whenever Clock is equal to 1 there are consecutive toggling. This condition is called as Race around condition. To put it in words, “ For JK flip-flop if J, K and Clock are equal to 1 the state of flip-flop keeps on toggling which leads to uncertainty in determining the output of the flip-flop. This problem is called Race around the condition. “’ This condition also exists in T flip-flop since T flip-flop also has toggling options.
Methods to eliminate race around condition
There are three methods to eliminate race around condition as described below:
Increasing the delay of flip-flop
The propagation delay (delta t) should be made greater than the duration of the clock pulse (T). But it is not a good solution as increasing the delay will decrease the speed of the system.
Use of edge-triggered flip-flop
If the clock is High for a time interval less than the propagation delay of the flip flop then racing around condition can be eliminated. This is done by using the edge-triggered flip flop rather than using the level-triggered flip-flop.
Use of master-slave JK flip-flop
If the flip flop is made to toggle over one clock period then racing around condition can be eliminated. This is done by using Master-Slave JK flip-flop.
- The delay between input and output is called
______.- Propagation delay
- Contamination delay
- Rise time
- Edge rate
- Propagation delay
- What are the methods to eliminate race around condition ?
- All of these
- Edge-triggered flip-flop
- Master-slave JK flip-flop
- Increase flip-flop delay
- All of these
- Which among the following is the race around condition ?
- J=1,K=1,Clock=1
- S=1,R=1,Clock=1
- J=0,K=0,Clock=0
- All of these
- J=1,K=1,Clock=1